OBJECTIVES
1. All economic systems must decide what to produce because
A. resources are not available. B. consumers want maximum satisfaction. C. resources are limited in supply. D. producers want maximum profit.
2. In any economic system, which of the following is not an economic problem?
A. What goods and services to produce. B. For whom to produce goods or services. C. What techniques of production to be adopted. D. Equal distribution of the goods and services.
3. Which of the following problems arises where there are more than one technically possible methods of production?
A. Where to produce. B. For whom to produce. C. How to produce. D. What to produce.
3. The Production Possibility Curve (PPC) indicates that as more of one good is produced
A. less of the other good is produced. B. the same quantity of the other good is produced. C. more of the other good is produced. D. none of the other good is produced.
4. Which of the following best explains what to produce
A. How much goods are to be produced. B. The combination of resources to be used. C. Which goods and services to be produced. D. How many wants are to be satisfied.
5. Points outside a production possibility curve indicate
A. unattainable production levels. B. attainable production levels. C. inefficient, but attainable production levels. D. optimum production levels.
6. The basic problem that Economics attempts to solve is the
A. ranking of goods and services. B. pricing of goods and services. C. scarcity of resources. D. foregoing of alternatives.
7. A basic economic problem of any society is
A. high level of illiteracy. B. irregular power supply. C. population growth. D. resource allocation.
8. Which of the following is related to resource allocation in an economy?
A. How to produce. B. What to produce. C. For whom to produce. D. Efficient use of inputs.
9. Most of the problems of economies arise as a result of
A. competing demands for scarce resources. B. increase in the demand for more goods and services. C. the desire of producers to supply more goods and services. D. the need to reduce the level of poverty.
10. A society that operates below the production possibility curve is using its productive resources
A. optimally. B. efficiently .C. inefficiently. D. maximally.
11. Economic problems arise mainly as a result of
A. inaccurate statistical data in West Africa. B. excessive wastage of available resources. C. lack of foresight on the part of resource user. D. limitations in availability of resources.
12. An outward shift of the production possibility curve shows that
A. production is shifting to the right. B. resources are underutilized. C. economic growth has taken place. D. factors of production are moving outward.
13. In a market economy, the problem of what goods to produce is solved primarily by
A. directives of the government. B. the pattern of consumer’s spending. C. producers of consumer goods. D. people producing what they want.
14. A society that is on its production possibility curve
A. has attained full employment but not full production. B. has attained full production but not full employment. C. is using its resources inefficiently. D. has attained both full employment and full production.
15. Economic problems arise because
A. resources are scarce relative to wants. B. man is insatiable. C. money is scarce. D. man engages in too many economic activities.
16. When all factor inputs are reduced by half, the production possibility curve will shift
A. outwards. B. inwards. C. downwards. D. upwards.
17. Every society strives to pursue all the following economic objectives except
A. increased production. B. price stability. C. an inequitable distribution of income. D. sustainable growth and development.
18. When all factor inputs are doubled the production possibility curve will
A. shift from left to right and return to its original position. B. shift from left to right. C. remain in its former position. D. shift from right to left.
19. The decision on what to produce is a problem in
A. all economic systems. B. a mixed economic system only. C. a democratic socialist economy only. D. a free enterprise system only.
20. The outward shift of the production possibility curve could be due to
A. military conquest. B. increased money supply. C. inflation. D. economic growth.
21. Economic problems arise in all societies because
A. resources are mismanaged by leaders. B. there is no proper planning. C. resources are not in adequate supply. D. the services of economists are not employed.
22. Which of the following is not emphasized in a production possibility curve
A. Scarcity of resources. B. Economic development. C. Inefficiency in the use of resources. D. Unemployment of labour.
23. The actual output of an economy is the output
A. which would exist if all resources were fully employed. B. produced by currently employed labour capital and land. C. produced in the consumer goods sector. D. produced in the capital goods sector.
24. The decision to consume more of one product will under normal circumstances imply that
A. more of another product will be consumed. B. less of something else will be consumed. C. no other product will be consumed. D. decision-making is basic in Economics.
25. The fundamental economic problem in every society is
A. the large number of the unemployed. B. inadequate supply of money. C. corruption and mismanagement. D. limited supply of productive resources.
26. A point X inside a production possibility curve indicates that
A. resources are fully utilized. B. the country is poor. C. some resources are idle. D. resources are not available.
27. When the production possibility curve shifts outwards, the economy experiences
A. growth. B. over-production. C. inefficient use of resources. D. under-production.
28. There is unemployment of resources when production is
A. within the production possibility curve. B. outside the production possibility’ curve. C. along the production possibility curve. D. adequate to meet market demand.
THEORY
1. Economic problems arise because a country’s resources are limited in relation to her unlimited wants. Identify and explain these economic problems.
2. (a) What is a production possibility curve? (b) Draw a production possibility curve and indicate any: (i) point P, where resources are fully utilized; (ii) point U, where resources are under-utilized; (lii) point X, where production is not feasible (c) Explain any two factors that can make production at point X feasible (d) Why is the production possibility curve negatively sloped?
3. The table below shows the various possible combinations of military and civilian goods produced by a country, using the available resources and technology. Use the table to answer the questions that follow.
| Military Goods (in tonnes) | Civilian Goods (in tonnes) |
| 0 20 | 200 160 |
| 40 | 120 |
| 60 | 80 |
| 80 | 40 |
| 100 | 0 |
(a) Draw the production possibility curve (PPC) (b) Indicate points S and K at which production is not feasible
(c)Indicate points M and N at which resources are not efficiently utilized (d) What does the downward slope of the
PPC indicate? (e) Why is production not feasible at points S and K?
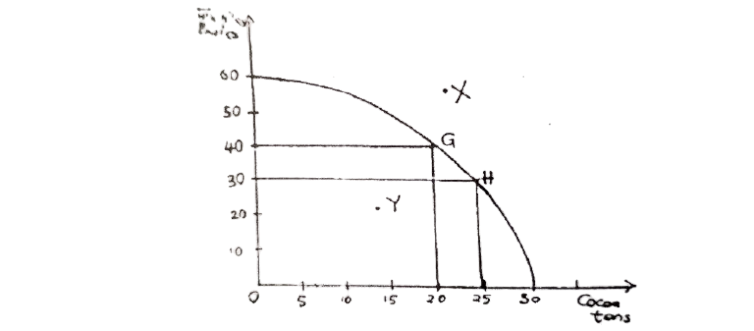
4. The figure below represents the production possibility curve of a nation. Use it to answer the questions that follow:
(a) What is the opportunity cost of (i) producing 30 units of cocoa; (ii) increasing textileproduction from 30 to 40bales? (b) Interpret the following points as found in the graph: (i) pointY; (ii) point G; (iii) point X. (c) List threeconditions that can enable the nation to produce atpoint X. (d) State two basic economic concepts illustrated in thediagram above. (e) (i) Defineproduction possibility curve (ii) What does the slope of the production possibilitycurve indicate?


