Introduction:
Soil is a vital component of the ecosystem, serving as the foundation for plant growth and a habitat for numerous organisms. In the WAEC Biology examination, understanding the properties, types, and significance of soil is essential for interpreting ecological data and solving related problems.
Key Concepts:
1. Definition of Soil:
Soil is the uppermost layer of the Earth’s crust, composed of mineral particles, organic matter, water, air, and living organisms. It supports plant life by providing nutrients, water, and a medium for root growth.
2. Soil Profile and Horizons:
A soil profile is a vertical section of the soil that reveals its layers, known as horizons:BYJU’S
- O Horizon (Organic Layer): Composed of decomposed organic matter.
- A Horizon (Topsoil): Rich in minerals and organic material; crucial for plant growth.
- B Horizon (Subsoil): Contains minerals leached from the topsoil and accumulates clay.
- C Horizon (Parent Material): Consists of weathered rock fragments.
- R Horizon (Bedrock): Unweathered rock layer beneath the soil.BYJU’S+5WAEC Online+5kaybeebio.com+5
3. Soil Types:
- Sandy Soil: Light, well-drained, and low in nutrients.
- Clayey Soil: Heavy, retains water, and rich in nutrients but poor in aeration.
- Loamy Soil: Balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay; ideal for most plants.
- Silty Soil: Smooth texture, retains moisture, and is fertile.9as.ng
4. Soil Properties:
- Texture: Determined by the proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles.
- Structure: Refers to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates.
- Porosity: Indicates the volume of pores or spaces within the soil.
- Permeability: Measures how easily water and air move through the soil.
- pH Level: Determines the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, affecting nutrient availability.9as.ng
5. Soil Formation Factors:
- Parent Material: The underlying geological material from which soil develops.
- Climate: Temperature and precipitation influence weathering and organic matter decomposition.
- Organisms: Plants, animals, and microorganisms contribute to soil formation and nutrient cycling.
- Topography: Slope and elevation affect drainage and erosion patterns.
- Time: Soil formation is a slow process that occurs over long periods.
6. Importance of Soil:
- Plant Growth: Provides essential nutrients and support for plants.
- Water Filtration: Filters and purifies water as it moves through the soil layers.
- Habitat: Supports a diverse range of organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and insects.
- Carbon Storage: Stores carbon, playing a role in regulating the Earth’s climate.9as.ng+1kaybeebio.com+1Nigerian Scholars+6WAEC Online+69as.ng+6
7. Soil Conservation Practices:
- Crop Rotation: Alternating crops to maintain soil fertility.
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops to prevent erosion and improve soil health.
- Terracing: Creating terraces on slopes to reduce runoff and erosion.
- Contour Plowing: Plowing along contour lines to minimize soil erosion.
- Mulching: Applying organic materials to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Study Tips:
- Understand Soil Profiles: Familiarize yourself with the different soil horizons and their characteristics.
- Compare Soil Types: Study the properties of various soil types and their suitability for plant growth.
- Practice Diagrams: Draw and label soil profiles to reinforce your understanding.
- Review Past Questions: Use the questions below for study and practice.
- Engage in Practical Activities: Conduct simple experiments to observe soil properties firsthand.
Conclusion:
A thorough understanding of soil and its properties is crucial for success in the WAEC Biology examination. By studying the formation, types, and conservation of soil, students can appreciate its significance in the ecosystem and its role in supporting life.
OBJECTIVES
1. The capillarity of a soil refers to
A. the particle size of soil. B. how easily water passes through soil. C. how well water rises up in soil. D. proportion of water a soil holds.
2. Soil erosion could be prevented by
A. flooding a farmland. B. cover cropping. C. deforestation. D. leaving the soil bare.
3. Soil permeability refers to
A. how easily water passes through the soil. B. the proportion of air in the soil. C. the proportion of water the soil holds. D. how well water rises up the soil.
4. Leguminous crops are incorporated into crop rotation in order to
A. improve aeration of the soil. B. promote nitrogen fixation. C. increase the rate of soil formation. D. improve upon the water holding capacity the soil.
5. Which of the following practices improves crop yield in a clayey soil? Addition of
A. more water and humus. B. lime and humus. C. fertilizers. D. weedicides and fertilizers.
The diagram below is an illustration of an experimental set-up to demonstrate a property of soil. Study and answer questions 6 & 7
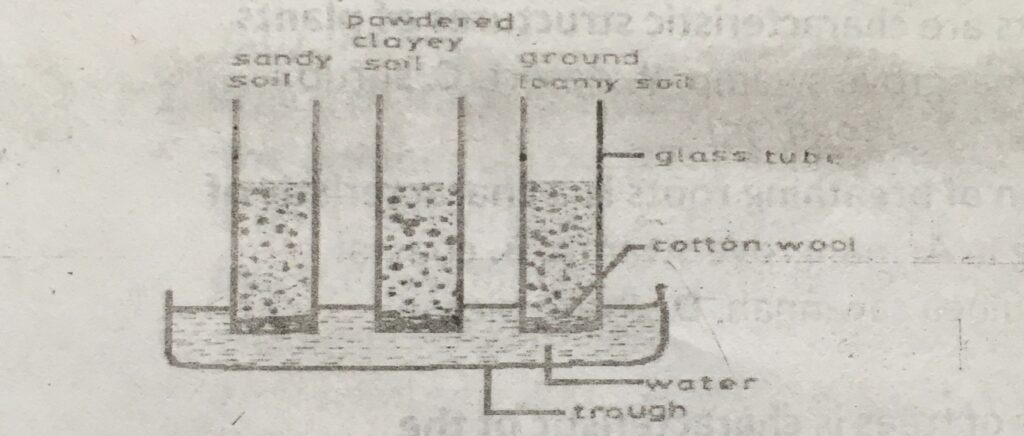
6. The property of soil demonstrated is
A. particle size. B. capillarity. C. colour, D. texture.
7. Which of the following statements would be a correct observation at the end of the experiment? Water moves
A. highest in sandy soil. B. lowest in loamy soil. C. to the same level in all soil types. D. highest in clayey soil.
8. Shrubs do not survive on newly weathered soils because
A. the top soil is shallow. B. drainage on such soil is poor. C. humus is absent from the soil. D. the soil tends to be sandy.
9. Which of the following statements is true about sandy soil? It
A. has limited air space. B. is light and easy to dig. C. drains slowly. D. is heavy and poorly aerated.
10. A sample of wet garden soil of known weight was heated to constant weight. The loss of weight is due to loss of
A. water. B. organic matter. C. water and organic matter. D. water and inorganic matter.
11. Which of the following is the correct method of collecting soil organism?
A. Heating the soil sample in an oven. B. Aerating the soil sample. C. Refrigerating the soil for some hours. D. Placing a lighted electric bulb over soil in a funnel.
12. Which of the following types of soil has the highest water-retaining capacity?
A. Clay, B. Laterite. C. Loam. D. Gravel.
13. Water rises most rapidly in
A. sandy soil. B. clayey soil, C. sandy-foam soil. D. loamy soil.
14. Which of the following will be the effect of waterlogged top soil on the roots of plants?
A. The waterlogged soil will stimulate rapid growth of root. B. There will be abundant supply of air for the growth of roots. C. The roots will absorb water rapidly. D. The roots will be starved of air.
15. The property of clay soil that prevents it from supporting thick vegetation is its
A. possession of chemically weathered granite rocks. B. inability to retain much water. C. tendency of becoming waterlogged. D. porosity and low water retention ability.
16. Which of the following farm practices can cause loss of soil fertility?
A. Mulching. B. Compost application. C. Use of fertilizers. D. Terracing.
17. Which of the following soil types retains the least amount of water
A. Loam: Bi Sand. C. Clay. D. Humus.
18. Which of the following phenomena affects plants growth in an alkaline soil?
A. Excessive plasmolysis. B. Excessive transpiration. C. Excessive sunlight. D. Poor drainage.
19. Loam is the best type of soil for crop production because
A. it has a high percentage of clay which. prevents leaching. B. it has high humus content. C. it is porous and has good water retention capacity. D. gravels which obstruct implements are absent from it.
20. A known weight of soil sample was oven-dried to obtain a constant weight. The loss in weight was due to loss of
A. organic matter only. B. water only. C. water and organic matter. D. inorganic matter and water.
21. Which of the following soil fertility improvement methods will have the most negative effect on the ecosystem if not controlled?
A. Application of N-P-K fertilizer. B. Shifting cultivation C. Mixed farming D. Crop rotation.
The diagram below is an illustration of an ecological instrument. Study it and answer questions 22 and 23.
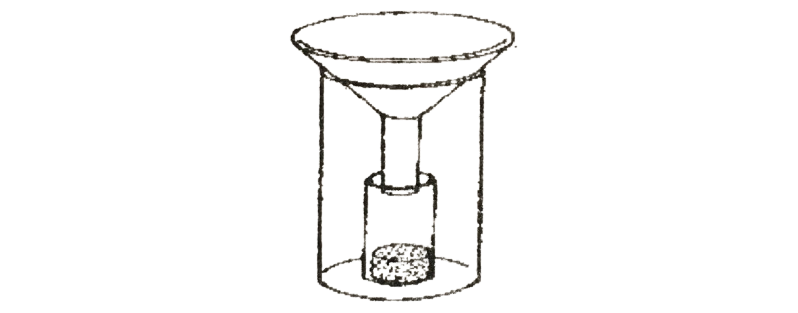
22. A disadvantage of the abiotic factor measured by the instrument is that it
A. is an agent of pollination. B. is necessary for germination. C. leads to flooding when in excess. D. is used for irrigation.
23. When the instrument is in use, it is usually placed
A. slightly above soil level. B. placed on a table. C. suspended in air. D. suspended on moving water.
24. Soil with the finest texture is
A. Silt. B. Clay. C. Sand. D. Gravel.
25. The property of clayey soil that prevents it from supporting thick vegetation is its
A. composition of chemically weathered granite rocks. B. inability to retain much water. C. tendency of becoming waterlogged. D. porosity and low water-retention ability.
26. Which of the following practices will not maintain soil fertility?
A. Preventing soil erosion B. Bush fallowing C. Leaving the land bare D. Planting cover crops.
The diagram below is an illustration of an experiment on sedimentation of soil. Use it to answer questions 27 and 28.
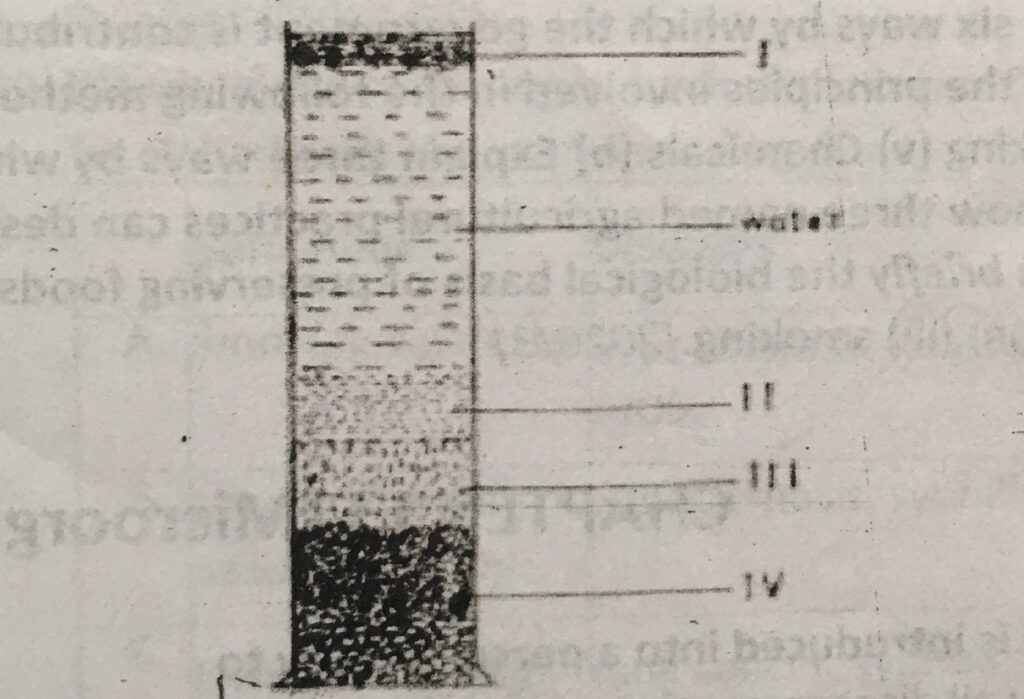
27. The organic component of the soil is labeled
A. I. B. II. C. III. D. IV.
28. The part labelled IV is
A. silt. B. sand. C. humus. D. clay.
29. Which of the following soil types have a high capillarity?
A. Sand and clay. B. Silt and clay. C. Silt and sand. D. Loam and sand.
THEORY
1. List five methods of conserving soil fertility
2. (a) Describe an experiment to compare the water-holding capacity of sandy, loamy and clayey soils (b) List three factors that may affect the water holding capacity of soil (c) State the characteristics of sandy and loamy soils (d) What type of vegetation does each support?


