Introduction: Pests and Diseases of Crops in WAEC Biology
Understanding crop pests and diseases is essential for WAEC Biology students, especially those preparing for topics related to agriculture, food production, and plant health.
WAEC often tests:
- Identification of common pests
- The types of damage they cause
- Methods of control and prevention
- Differences between pests and diseases
This guide provides key revision points and WAEC-style multiple-choice past questions to sharpen your exam preparation.
Quick Revision Notes on Crop Pests & Diseases
- Pests are animals or insects that damage crops (e.g., locusts, grasshoppers, weevils).
- Diseases are caused by pathogens like fungi, bacteria, or viruses (e.g., maize rust, cassava mosaic, rice blast).
Common Crop Pests:
- Weevils – attack stored grains
- Grasshoppers & Locusts – chew leaves of growing plants
- Stem borers – damage stems of maize
- Aphids – suck plant sap
Common Crop Diseases:
- Cassava Mosaic Virus (CMV) – discolors cassava leaves
- Maize Rust (fungal) – brownish patches on maize leaves
- Rice Blast (fungal) – affects rice leaves and stems
Control Measures:
- Use of pesticides or insecticides
- Crop rotation
- Proper storage methods
- Planting disease-resistant varieties
- Use of biological control agents
WAEC Past Questions on Pests & Diseases of Crops
1. Which of the following is a storage pest?
A. Grasshopper
B. Maize weevil
C. Stem borer
D. Armyworm
2. A major symptom of cassava mosaic disease is:
A. Black spots on leaves
B. Mottling and curling of leaves
C. Wilted stems
D. Root decay
3. Which of the following is not a method of controlling crop pests?
A. Use of pesticides
B. Crop rotation
C. Harvesting at the right time
D. Burning of healthy crops
4. Maize rust is caused by:
A. Bacteria
B. Virus
C. Fungus
D. Insects
5. The pest that damages maize by boring into the stem is:
A. Aphid
B. Armyworm
C. Maize weevil
D. Stem borer
6. Which of the following pests sucks sap from crops?
A. Grasshopper
B. Armyworm
C. Aphid
D. Caterpillar
7. Which is a biological control method for pests?
A. Spraying insecticides
B. Using predators like ladybird beetles
C. Burning of farms
D. Use of GMO crops
8. Crop rotation is effective against:
A. Viral diseases
B. Soil-borne pests and diseases
C. Insect-borne diseases only
D. Animal pests
9. Which of the following is a fungal disease?
A. Cassava mosaic
B. Rice blast
C. Maize streak
D. Tomato wilt (bacterial)
10. A good way to prevent pest attack in stored grains is to:
A. Store them in plastic bags
B. Leave them in open air
C. Treat them with insecticides
D. Use wet containers
Get full questions below…
WAEC Exam Tips:
- Know examples of both pests and diseases.
- Memorize the causes (fungus, virus, insect).
- Learn symptoms and control methods.
- Practice identifying pests/diseases from diagrams or descriptions.
Objectives:
1. The following organisms are pests of plants except
A. birds.
B. nematodes.
C. bacteria.
D. rodents.
2. The use of predators or parasites to control pests in the farm is known as
A. predator control.
B. chemical control,
C. biological control.
D. animal control.
3. Which of the following is the underlining principle in the adoption of biological control of pests?
A. Knowledge of agricultural practices by the farmer,
B. Relationship between plants and animal.
C. The presence of poisonous chemicals in the farm.
D. The predator-prey relationship in the ecological community.
The diagram below is an illustration of the life cycle of an insect. Study it and answer questions 4 and 5.
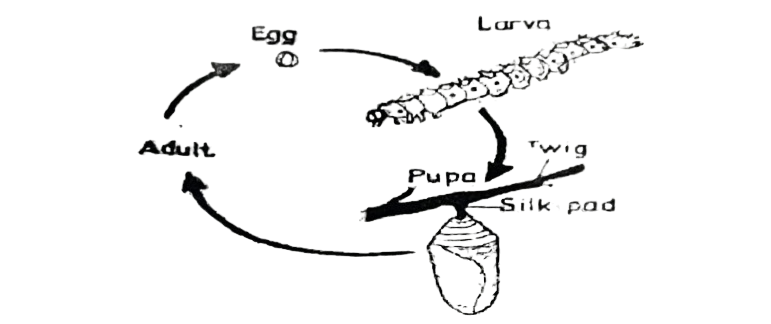
4. The adult insect in this life cycle is
A. housefly.
B. butterfly.
C. cockroach.
D. mosquito.
5. The larva is also known as
A. nymph,
B. maggot.
C. caterpillar.
D. chrysalis.
6. Predators are beneficial in pest control because they
A. are natural enemies of small mammals.
B. devour farm animals.
C. feed on pests of crops.
D. prey by game animals.
7. Which of the following plant diseases is indicated when grains of cereals are covered with a mass of spores?
A. Smut.
B. Mosaic.
C. Maize streak.
D. Fungal blast.
8. Pests can be controlled without the subsequent danger of polluting the ecosystem by
A. introducing a population of species similar to that of the pest.
B. increasing the population of the natural enemies of the pest.
C. eliminating the natural enemies of the pest.
D. keeping the population of natural enemies of the pest constant.
9. Which of the following measures is most likely to cause a damage to the ecosystem in the control of pests and weeds?
A. Use of ladybird insects to feed on aphids.
B. Introduction of bacterium to kill larvae of butterfly.
C. Introduction of Tilapia fish in ponds to feed on mosquito larvae.
D. Spraying insecticides to destroy cotton strainers in a cotton-field.
10. When a farmer sprays crops with a pesticide, the pesticide becomes
A. poisonous to all plants.
B. is broken down by soil algae.
C. easily washed down into lakes and rivers.
D. absorbed by bodies of mammals.
Use the list of insects below to answer questions 11 and 12.
I- Cotton Stainer
II- Honeybee
III- Termite
IV- Weevil
11. The insects whose activities are both beneficial and harmful to humans are
A. I and II.
B. II and III.
C. II and IV.
D. Ill and IV
12. Which of the insects destroys grains?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV.
THEORY
1. (a) Name two pests and two diseases that can attack plant crops.
(b) State three ways of controlling plant diseases.
2. Name two viral diseases of plants.
More Revision Posts:
- WAEC Biology Questions on Pollution
- WAEC Biology Questions on Conservation of Natural Resources
- WAEC Biology Questions on Nutrition & Photosynthesis
Found this useful? Don’t forget to share with other WAEC candidates and leave a comment below!


