In Biology, population studies focus on the number of individuals of a species in a given area. Understanding the factors affecting population size is vital for students preparing for WAEC and other senior school exams. This topic covers both biotic and abiotic factors that can increase or decrease population numbers.
This post presents important WAEC-standard questions, model answers, and key points to help you study smarter and score higher.
What Is Population in Biology?
In ecology, a population refers to a group of organisms of the same species living and interacting in a particular geographical area at a specific time.
The size and health of a population can be influenced by many factors, broadly grouped into:
- Biotic factors (living things like predators or food supply)
- Abiotic factors (non-living things like temperature or rainfall)
WAEC Biology Questions on Factors Affecting Population
Question 1:
List four abiotic factors that affect population.
Model Answer:
- Temperature
- Rainfall
- pH of soil or water
- Availability of sunlight
Question 2:
Explain how competition affects population size.
Model Answer:
Competition occurs when individuals or species compete for limited resources such as food, water, space, or mates. When competition is intense, weaker individuals may die or migrate, reducing the population size.
Question 3:
Mention three biotic factors that can affect the population of an organism.
Model Answer:
- Predation
- Diseases
- Availability of food
Question 4:
State two ways in which drought can affect population.
Model Answer:
- Reduced water availability can lead to death of plants and animals.
- It can cause migration of animals in search of water, reducing the local population.
Question 5:
Differentiate between immigration and emigration.
Model Answer:
- Immigration is the movement of individuals into a population, increasing its size.
- Emigration is the movement of individuals out of a population, decreasing its size.
Key Factors Affecting Population
1. Availability of Food:
Abundant food increases population growth, while scarcity reduces it.
2. Predation:
Predators reduce the population of their prey.
3. Diseases:
Can reduce population by causing death or reducing reproduction.
4. Climatic Conditions:
Rainfall, temperature, and humidity influence survival and reproduction.
5. Human Activities:
Deforestation, pollution, urbanization, and farming can drastically affect population sizes.
6. Natural Disasters:
Floods, earthquakes, and wildfires can cause sudden population decline.
Try This WAEC-Style Practice Questions
The diagram below illustrates an ecological instrument.
Use it to answer questions 1 & 2
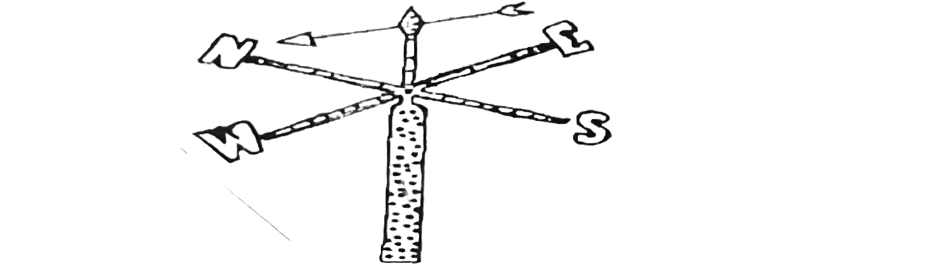
1. The instrument is
A. an anemometer.
B. a hygrometer.
C. a barometer.
D. a wind vane.
2. The instrument is used to measure the
A. direction of wind.
B. speed of wind.
C. air pressure in a habitat.
D. turbidity of water.
3. The following are abiotic components of the ecosystem except
A. bacteria.
B. topography.
C. water.
D. wind.
4. Which of the following instruments would be most appropriate in comparing the air pressure at different places in a habitat?
A. Hygrometer.
B. Barometer.
C. Photometer.
D. Air pressure disc.
5. Which of the following physical factors is likely to affect the distribution of plants in a pond? A. Light.
B. Humidity.
C. Wind.
D. Temperature.
6. Which of the following instruments is used to measure wind speed?
A. Thermometer.
B. Barometer.
C. Hygrometer.
D. Anemometer.
Plant A was seen to appear as plant B after seven hours.
Study the diagrams carefully and answer questions 7 & 8
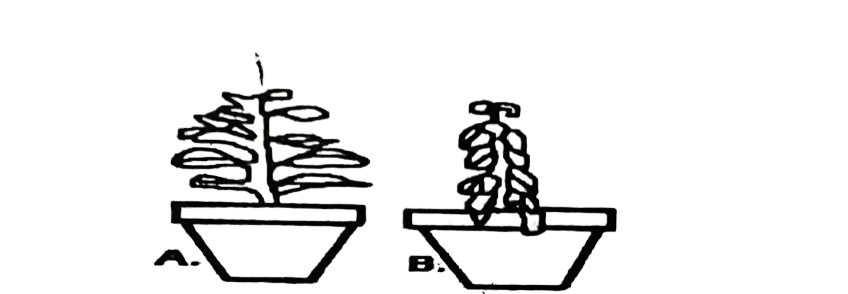
7. The term that can be used to describe what happened to plant after seven hours is
A. wilting.
B. competition.
C. transpiration.
D. osmosis.
8. The environmental factors responsible for the condition in plant are
A. Low humidity and high temperature.
B. high humidity and low temperature.
C. high humidity and high temperature.
D. high humidity and high temperature.
9. The direction of wind is determined by
A. An anemometer.
B. a secchi disc.
C. a wind vane.
D. a barometer.
10. A hygrometer is used for measuring
A. relative humidity.
B. specific gravity.
C. light intensity.
D. turbidity.
11. The physical and chemical factors which affect the life of organisms in an environment are described as
A. biotic.
B. edaphic.
C. abiotic.
D. physiographic.
12. Which of the following instruments can be used to measure relative humidity?
A. Anemometer.
B. Hygrometer.
C. Wind gauge.
D. Barometer.
13. Which of the following is not promoted by high wind speed?
A. Rill erosion.
B. Weathering of parent rock.
C. Breeding of plant.
D. Opening of stomata.
14. Wind speed is measured with
A. a maximum- minimum thermometer.
B. a hygrometer.
C. a wet and dry bulbs hygrometer.
D. an anemometer.
15. The speed of wind is measured using the
A. wind vane.
B. anemometer.
C. photometer.
D. barometer.
16. The following are abiotic components of/an ecosystem except
A. temperature.
B. oxygen.
C. bacteria.
D. air.
17. Which of the following instruments is used to determine the turbidity of water
A. Hygrometer.
B. Hydrometer.
C. Secchi disc.
D. Rain gauge.
18. The diagram below is an illustration of organisms in an air-tight aquarium. The most important factor needed by the organisms is
A. light energy.
B. low humidity.
C. oxygen.
D. nitrate.

19. The Tullgren’s funnel is used to
A. extract minute soil organisms.
B. measure the amount of rainfall.
C. collect water from habitats.
D. pour liquid into containers with narrow mouth.
20. The factors which determine the type of vegetation in particular habitat will support are related to the following except
A. nature of the soil particles.
B. amount of rainfall.
C. mineral content of the soil.
D. depth of the water-table.
21. Which of the following is an abiotic factor which affects a population?
A. Predator.
B. Parasite.
C. Consumer.
D. Temperature.
22. The abiotic factor which determines the depth to which light penetrates in a pond is
A. current.
B. turbidity.
C. wind.
D. salinity.
23. Which of the following instruments is used to measure the speed of a stream
A. Simple float.
B. Secchi disc.
C. Quadrat frame.
D. Rain gauge.com
24. Which of the following is an abiotic factors?
A. Predation.
B. Rainfall.
C. Cropping.
D. Grazing.
25. The maximum and minimum thermometer is used to measure
A. light intensity.
B. highest and lowest temperature of the day.
C. atmospheric pressure.
D. highest and lowest amount of rainfall in a month.
Use the graphs below to answer the question
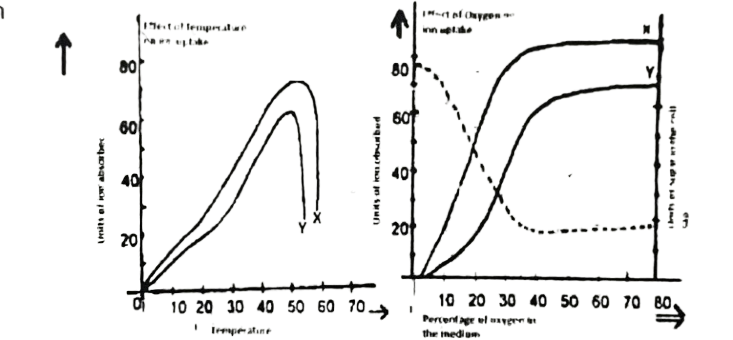
26. Which of the temperature ranges will likely favour the plant best?
A. 0-10°C.
B. 15-20°C.
C. 30-40°C.
D. 45-50°C.
27. Which of the following is not a biotic factor?
A. Parasites.
B. Predators.
C. Grazers.
D. Pressure.
28. The secchi disc is used to measure
A. speed of flow of water.
B. specific gravity of water.
C. turbidity of water.
D. depth of water.
29. Soil factors in an ecosystem are referred to as
A. topographic.
B. climatic.
C. biotic.
D. edaphic.
30. Predation is an example of a factor in an ecological system referred to a
A. edaphic.
B. topograhic.
C. abiotic.
D. biotic.
31. The activities of an organism which affect the survival of another organism in a habitat can be described as
A. biotic factors.
B. climatic factors.
C. physiographic factors.
D. edaphic factors.
32. The numbers in a population would rise, if there was an increase in the
A. spread of disease.
B. number of deaths.
C. number of predators.
D. amount of food available.
33. Natality is a factor affecting population density because it involves
A. increase in population due to immigration.
B. increase in population due to emigration.
C. the number of mature females in the population.
D. the number of females in the population.
34. The density-dependent factors that operate to and regulate a population size may include the following except
A. shortage of food supply.
B. fire outbreak.
C. spread of diseases.
D. increased competition.
35. Which of the following factors does not control population growth?
A. Food shortage
B. Emigration.
C. Abundance of food.
D. Predation.
36. Which of the following will have the least effect on the rate of change of the numbers in a population?
A. Food supply.
B. Mutation.
C. Predation.
D. Disease.
37, Density mortality rate birth rates are the factors that affect
A. Population.
B. dominance.
C. cover.
D. habitat.
38. Which of the following processes is not due to interaction between the biotic and abiotic
components of an ecosystem?
A. Soil nutrient depletion
B. Condensation.
C. Decomposition.
D. Osmosis.
39. The salinity of a brackish habitat
A. increases immediately after rainfall.
B. increases at the end of the rainy season.
C. decreases with an increase in the number of organisms.
D. increases during the dry season.
40. Which of the following instruments is not used in measuring abiotic factors in a habitat?
A. Thermometer.
B. Microscope.
C. Hygrometer.
D. Wind vane.
THEORY
1. Name one instruments each used for measuring:
(i) relative humidity;
(ii) wind speed.
2. State five effects of high temperature on a terrestrial habitat.
3. (a) Name one instrument used for collecting:
(i) soil organisms from a soil sample
(ii) tiny Insects from a leaf or a stem.
(b) Make a diagram 6cm – 8 cm long of the instrument named in
(a)(ii) and label fully.
4. List three gases in the atmosphere with their percentage composition.
5. List two biotic and abiotic factors each that affect population growth.
6. List three biotic factors.
7. (a) List three instruments used in the measurement of different ecological factors
(b) Briefly state what each instrument listed in (a) above is used for.
8. (a) Define the term population
(b) What are the effects of food shortage on a population?
9. State the importance of each of the following in a population and explain how each affects the growth of a population;
(i) competition;
(ii) pathogens;
(iii) water.
10. State four problems that may be caused by human overpopulation.
11. Explain four factors which affect population size.
12. Write short note on population.
13. Describe how temperature as an ecological factor can be measured.


