Summary of the Topic:
Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms without being consumed in the process. They are vital for various physiological functions, including digestion, metabolism, and cellular activities.
Key points to understand:
- Nature of Enzymes: Mostly proteins that function under specific conditions.
- Specificity: Each enzyme acts on a particular substrate.
- Optimal Conditions: Enzymes have specific temperature and pH ranges where they function best.
- Inhibition: Certain substances can inhibit enzyme activity.
- Industrial Applications: Enzymes are used in industries like brewing, baking, and pharmaceuticals.
Key Concepts Explained:
1. Characteristics of Enzymes:
- Biological Catalysts: Speed up reactions without being used up.
- Specificity: Each enzyme acts on a specific substrate.
- Optimal Temperature: Most human enzymes function best at ~37°C.
- Optimal pH: Different enzymes have different pH optima (e.g., pepsin at pH 2).
- Reusability: Enzymes can be used repeatedly.
- Sensitivity: High temperatures or extreme pH can denature enzymes.
2. Enzyme Action Mechanism:
- Lock and Key Model: The enzyme’s active site fits the substrate precisely.
- Induced Fit Model: The enzyme adjusts its shape to fit the substrate upon binding.
3. Enzyme Inhibition:
- Competitive Inhibition: Inhibitor resembles the substrate and competes for the active site.
- Non-Competitive Inhibition: Inhibitor binds elsewhere, altering the enzyme’s shape.
4. Industrial Applications:
- Brewing: Enzymes break down starches into sugars.
- Baking: Enzymes improve dough quality.
- Pharmaceuticals: Enzymes assist in drug formulation.
Example WAEC-Style Questions (With Explanations):
Q1: Pepsin is secreted as an inactive precursor called pepsinogen because:
A. Pepsin as an enzyme is quickly destroyed by the alkaline food from the mouth.
B. All digestive enzymes pass through a precursor stage.
C. Pepsin is a proteolytic enzyme and might attack the stomach tissues.
D. Pepsin is not required in large quantities.
Answer: C. Pepsin is a proteolytic enzyme and might attack the stomach tissues.
Explanation: Pepsinogen prevents the enzyme from digesting the stomach lining before activation.
Q2: Which of the following digestive enzymes would be greatly affected if the liver fails to produce bile?
A. Amylase
B. Cellulase
C. Lipase
D. Protease
Answer: C. Lipase
Explanation: Bile emulsifies fats, aiding lipase function.
Q3: Enzymes can be inactivated by certain chemical substances in the body called:
A. Catalysts
B. Inhibitors
C. Substrates
D. Activators
Answer: B. Inhibitors
Explanation: Inhibitors interfere with enzyme activity.
Q4: Which of the following pH values is the best for the action of the enzymes – renin and pepsin in the stomach?
A. pH 2
B. pH 7
C. pH 8
D. pH 9
Answer: A. pH 2
Explanation: Pepsin and renin function optimally in acidic conditions.
Q5: Which of the following enzymes is active in the duodenum?
A. Pepsin
B. Renin
C. Trypsin
D. Amylase
Answer: C. Trypsin
Explanation: Trypsin is secreted by the pancreas and acts in the duodenum.
Q6: The enzyme that acts on milk in the stomach is:
A. Invertase
B. Trypsin
C. Diastase
D. Renin
Answer: D. Renin
Explanation: Renin curdles milk in the stomach, aiding digestion.
Q7: Which of the following statements is true?
A. Ptyalin acts on proteins to give amino acid.
B. Lactase acts on maltose to give amino acid.
C. Pepsin acts on proteins to give peptide.
D. Peptide acts on starch to give maltose.
Answer: C. Pepsin acts on proteins to give peptide.
Explanation: Pepsin breaks down proteins into peptides.
Q8: An enzyme reaction may begin to decline when:
A. The optimum temperature is attained.
B. The pH of the medium is altered.
C. There is an increase in substrate concentration.
D. The atmospheric pressure is altered.
Answer: B. The pH of the medium is altered.
Explanation: Enzymes have specific pH ranges; deviations can reduce activity.
Q9: Which of the following food substances is incorrectly linked to its enzyme?
A. Protein – trypsin
B. Fat – lipase
C. Sucrose – pepsin
D. Starch – amylase
Answer: C. Sucrose – pepsin
Explanation: Pepsin acts on proteins, not sucrose.
Q10: Which of the following enzymes does not belong to proteases?
A. Sucrase
B. Pepsin
C. Trypsin
D. Erepsin
Answer: A. Sucrase
Explanation: Sucrase breaks down sugars, not proteins.
Study Tips:
- Understand Enzyme Specificity: Learn which enzymes act on which substrates.
- Memorize Optimal Conditions: Know the pH and temperature ranges for enzyme activity.
- Practice Diagrams: Visualize the lock and key model and enzyme-substrate interactions.
- Relate to Real-Life Applications: Understand how enzymes are used in industries.
- Solve Past Questions: Regular practice helps in familiarizing with question patterns.
Conclusion:
A solid grasp of enzyme functions and characteristics is essential for excelling in WAEC Biology. To reinforce your understanding, proceed to the WAEC past questions provided below, which offer practical application of the concepts discussed.
OBJECTIVES
1. Pepsin is secreted as an inactive precursor called pepsinogen because
A. pepsin as an enzyme is quickly destroyed by the alkaline food from the mouth.
B. all digestive enzymes pass through a precursor stage.
C. pepsin is a proteolytic enzyme and might attack the stomach tissues.
D. pepsin is not required in large quantities.
2. Adenine pairs with thymine because
A. the two occur in the same nucleic acid.
B. one is a strong base and the other a weak base.
C. two purine bases easily pair up.
D. one is a purine base and the other a pyrimidine.
3. Which of the following digestive enzymes would be greatly affected if the liver fails to produce bile?
A. Amylase,
B. Cellulase.
C. Lipase.
D. Protease.
4. The name of the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate at the beginning of glycolysis is
A. phosphofructokinase.
B. glucose-isonterase.
C. hexokinase.
D. glucose-6-kinase.
5. Enzymes can be inactivated by certain chemical substances in the body called
A. catalysts.
B. inhibitors.
C. substrates.
D. activators.
6. Which of the following enzymes is not one of the main classes of enzymes?
A. Sucrase.
B. Amylases.
C. Proteases.
D. Lipases.
7. Which of the following food substances is incorrectly linked to its enzyme?
A. Protein-trypsin.
B. Fat-lipase.
C. Sucrose pepsin.
D. Starch-amylase.
8. Which of the following enzymes does not belong to proteases?
A. Sucrase.
B. Pepsin
C. Trypsin.
D. Erepsin.
9. Which of the following pH values is the best for the action of the enzymes – renin and pepsin in the
stomach?
A. pH 2.
B. pH 7.
C. pH 8.
D. pH 9.
10. Which of the following enzymes is active in the duodenum?
A. Pepsin.
B. Renin.
C. Trypsin.
D. Amylase.
11. Which of the following juices contains the enzyme ptyalin
A. Gastric juice.
B. Pancreatic juice.
C. Succus.
D. Saliva.
12. If an enzyme works best in an acid medium, in which of the following parts of the human gut is the pH best for enzyme activities? In the
A. ileum, pH 9.0.
B. stomach, pH 2.0.
C. duodenum, pH 7.0.
D. mouth cavity; pH 8.0.
13. The enzyme that acts on milk in the stomach is
A. invertase.
B. trypsin.
C. diastase.
D. renin.
14. Which of the following statements is true?
A. Ptyalin acts on proteins to give amino acid.
B. Lactase acts on maltose to give amino acid.
C. Pepsin acts on proteins to give peptide.
D. Peptide acts on starch to give maltose.
15. Which of the following statements about a mixture of a protein-digesting enzyme and starch solution would be correct? The protein-digesting enzyme
A. Has no effect on the starch solution.
B. Leads to the production of amino acids.
C. Leads to the production of glucose.
D. Digests the starch.
16. An enzyme reaction may begin to decline when
A. the optimum temperature is attained.
B. the pH of the medium is altered.
C. there is an increase in substrate concentration.
D. the atmospheric pressure is altered.
Diagram J is a protease while diagrams K, L, M and N are food substances. Study them and answer questions 17 to 19.
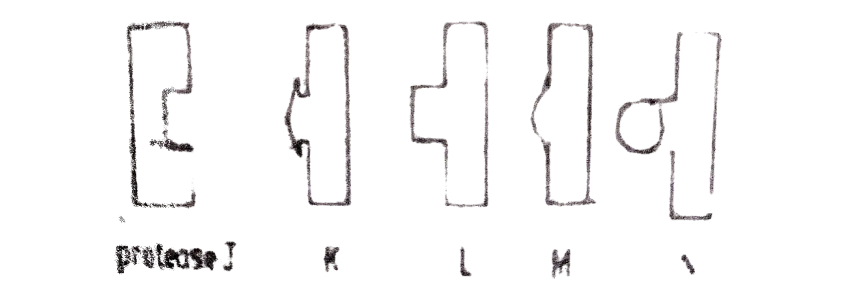
17. Which of the illustrated food substances would form a reaction with protease J?
A. K
B. L
C. M
D. N
18. Protease J would react with the particular illustrated substance because enzymes
A. are denatured at a high frequency.
B. are specific in their action.
C. remain unchanged after a reaction.
D. speed up the rate of chemical reaction.
19. After a reaction between protease J and the food substance, the end-product would be
A. fatty acids.
B. glucose.
C. amino acids.
D. water.
THEORY
1. In a tabular form, state the source, substrate and end products of the following enzymes (i) ptyalin; (ii) pepsin; (iii) lipase.
2 (a) State four characteristics of enzymes (b)List two examples of digestive enzymes produced in the duodenum of humans; (c) Name the substrate for each enzyme listed in (b); (d) State the products of each enzyme activity in (b) above.
3. (a) State three characteristics of enzymes (b) In a tabular form indicate the source, substrate acted upon and the product of the following enzymes: ptyalin, pepsin.
4. (a) Name one organelle in a living cell that produces enzyme (b) Mention two enzymes that act on proteins.
5. (a) Define enzymes (b) State six characteristics of enzymes.


