Introduction
This topic explores how genetic principles are applied and how probability underlies inheritance patterns. It’s essential for understanding how traits are passed down and how likely certain genetic outcomes are—key for excelling in the WAEC Biology examination.
Key Concepts
1. Genetic Applications
Genetics is applied in many important fields, such as:
- Determining paternity
- Blood transfusion compatibility
- Screening for genetic disorders
- Crime detection
2. Mendel’s Laws and Probability
- Law of Segregation: Alleles separate so each gamete carries only one copy.
- Law of Independent Assortment: Genes for different traits are inherited independently.
Probability is used to predict inheritance patterns using tools like Punnett squares.
3. Monohybrid Crosses
Crosses between individuals heterozygous for a trait typically yield offspring in a 3:1 phenotypic ratio and 1:2:1 genotypic ratio.
4. Blood Group Inheritance
Blood types follow Mendelian patterns, with group AB showing co-dominance, and group O being recessive.
5. X-linked and Sex-linked Traits
Traits like haemophilia follow sex-linked inheritance patterns; probability helps calculate risk for sons and daughters based on parental genotypes.
6. Advanced Probability in Genetics
- Bayesian methods: Update probabilities of genotypes or carrier status based on new evidence (e.g., family medical history).
- Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium: Uses allele frequencies (p + q = 1; p² + 2pq + q² = 1) to predict population genotype distributions under ideal conditions.
Study Tips
- Master Mendel’s laws and understand how they relate to probability.
- Practice Punnett square calculations for monohybrid and dihybrid crosses.
- Use real-world examples—like blood groups and sex-linked diseases—to apply your knowledge.
- Incorporate probability rules (multiplication for “and”, addition for “or”) when predicting phenotypic or genotypic outcomes.
- Review past questions below to test your understanding and apply concepts.
Conclusion
Applications of genetics and probability are at the heart of understanding inheritance. Grasping these concepts will strengthen your performance in WAEC Biology and deepen your appreciation of how traits are passed through generations.
Use the questions below to reinforce your learning.
OBJECTIVES
1. A woman with blood group A gives birth to a child with blood group O. Which of the following blood groups cannot belong to the father?
A. A.
B. B.
C. AB.
D. O.
2. When a man who is Rh-positive marries a woman who is Rh-negative there will be incidence of
A. still births.
B. sicklers.
C. Albinos.
D. living children.
3. Which of the following traits must be considered in marriage counselling?
A. Height.
B. Fingerprints.
C. Rhesus factor.
D. Colour of skin.
4. A cross between two parents produced four offspring with blood group AB, BB, BO and AO. What is the blood group of their parents?
A. AA and BO.
B. BB and AO.
C. AB and BO.
D. AB and AO.
5. A sick baby was successfully transfused with blood from the father who has blood group AB. What is the group of the sick baby
A. A. B.
B. C. AB.
D. O.
The illustration below represents a cross between a colour blind male and a normal female Study it carefully and answers questions 6 & 7.

6. What is the genotypic ratio of carrier females to normal males in the cross
A. 1:1.
B. 2:3.
C. 3:4.
D. 4:1.
7. Which of the genotypes are carriers of colour blindness?
A. I and II only.
B. I and III only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II
8. A person with blood group O can be given blood from persons who have blood belonging to
A. group O only.
B. group A only.
C. groups A and O.
D. groups A, B and O.
9. Mr Andrew, his wife and child belong to blood groups A,
B and O respectively. The genotypes of both parents are
A. 11° and 11.
B. 1^1 and 1818.
C. 1^1 and 1^18.
D. 11° and 181°.
10. A man with blood group I^IA is married to a woman with blood group 1°. The blood group of their son is likely to be
A. A.
B. O.
C. B.
D. AB.
11. Which of the following human traits in a class of school children may give an approximate normal distribution curve when the variation is plotted?
A. Blood groups.
B. Ear shapes.
C. Sex distribution.
D. Heights.
12. Variation is important in human life and can be used for the following activities except
A. crime detention.
B. population distribution.
C. blood transfusion.
D. determination of paternity.
13. Fingerprints are useful in crime detection because
A. the police have sophisticated fingerprint machines.
B. thieves may leave their prints at the scene of a crime.
C. no two people have the same fingerprint.
D. fingerprints are easy to make.
14. Which of the following diseases can be inherited?
A. Pneumonia.
B. AIDS.
C. Sickle cell anaemia.
D. Goitre.
15. Assuming that A is the gene for normal skin colour and is dominant, while a is the gene for albinism and is recessive, what is the likely genotype of the couple which had 50% normal and 50% albino offspring?
A. AA, aa.
B. Aa, aa.
C. AA, Aa.
D. Aa, Aa.
16. The genotype ratio of the offspring of a hybrid is 1: 2: 1. which of the following laws illustrates this ratio?
A. Use and disuse.
B. Dominance.
C. Segregation.
D. Linkage.
17. If red is dominant to white and homozygous red pea-plants are crossed with homozygous white pea-plants, the first filial generation will have
A. 2 red flowers, 2 white flowers.
B. 4 réd flowers.
C. 4 white flowers.
D. 4 pink flowers.
18. A man’s blood group is AB. What is the probability of the man giving birth to a child with blood group O?
A. 0%.
B. 25%.
C. 50%.
D. 100%.
19. A man who suffers from haemophilia marries a woman who is a carrier, what percentage of their children are likely to be haemophilia?
A. 25%.
B. 50%.
C. 75%.
D. 100%.
20. A man who is heterozygous for the disease haemophilia marries a woman who is double recessive
of haemophilia. What percentage of their offspring would have the disease?
A. 0%
B. 25%.
C. 50%.
D. 75%.
21. Two tall plants were crossed; some of their off springs 36. Two yellow-flowered hybrid plants each
were tall and others short the possible phenotype of and Tt. D. Tt and TT. carrying a cape recessive factor for flowers with green colour were the parent plants were
A. TT and TT.
B. TT and tt.
C. Tt crossed.
22. What is the probability of producing a child of blood 2. B. 1 in 3. C. 1 in 4. D. 1 in 5 group O by a woman of blood group O and a man of 37. Which of the following diseases is commonly observed
blood group A?
A. 25%.
B. 50%.
C. 75%.
D. 100%.
23. A man heterozygous for albino gene marries a woman who is also heterozygous for the gene. Both have normal skin colour. The probability that they will have an albino child is A. B. C. D.2
in human males and is sex-linked?
A. Beriberi.
B. Down’s syndrome.
C. Sickle-cell anaemia.
D. Colour blindness.
24. An albino man marries a normal woman (homozygous contrasting features such as tallness and shortness are for skin pigmentation). What is the probability that the people could have an albino child? A. 0%.
B. 0.5%.
C. 25%.
D. 60%.
25. What is the probability of a man of blood group AB married to a woman of blood group O producing a child of blood group O?
A. 0%.
B. 25%.
C. 50%.
D. 75%.
26. The defective cells involved in sickle-cell anaemia disease are
A. phagocytes.
B. lymphocytes.
C. erythrocytes.
D. thrombocytes.
27. Which of the following diseases is not hereditary?
A. Albinism.
B. Scabies.
C. Haemophilia.
D. Colour blindness.
28. What would be the phenotypic ratio of the offspring of a cross between a heterozygous dominant parent and a double recessive parent?
A. 1:2:1.
B. 1: 1.
C. 3:1.
D. 2:1.
29. The percentage probability that a normal male married to a carrier woman would have a haemophilic male child is
A. 35%.
B. 50%.
C. 75%.
D. 100%.
30. If a person has two alleles of the sickle cell anaemia gene, the person
A. is a heterozygous carrier of the disease.
B. is immune to the disease and cannot pass it on to an offspring.
C. has the disease.
D. is probably of Asian ancestry.
Two unconscious patients X and Y whose blood group genotypes are AO and AB respectively were transfused with blood from the same donor. Patient X immediately showed signs of difficulty in breathing while patient Y showed no negative reaction.
Use the information above to answer questions 31 & 32
31. Patients X and Y were likely transfused with blood of genotype
A. 00.
B. AO.
C. BO.
D. AA.
32. What should the hospital have done to prevent patient X from showing the symptom described above? Patient X should have
A. undergone an agglutination test.
B. been asked for the blood group.
C. been screened for HIV.
D. undergone malaria test.
33. In artificial selection, individuals without desirable traits may be prevented from mating by
A. outbreeding
B. sterilization.
C. inbreeding.
D. genetic engineering.
34. Two plants with red flowers were back crossed, which of the following results indicate that the plants are heterozygous red flowers, where red flowers are dominant?
A. 75% red and 25% white.
B. 50% red and 50% white.
C. 100% white.
D. 100% red.
35. In a case of complete dominance, what is the phenotypic ratio of the cross Bb X Bb; where B =black
and b = white?
A. 1 black : 1 grey 2 whites.
B. 1 black: 3 whites.
C. 1 black, 2 blues: 1 white.
D. 3 blacks: 1 white.
36. If a boy has blood type O and his mother has blood type F. what is the genotype of his father?
A. BB.
B. AA.
C. AO.
D. AB.
37. When gametes from pure breeding parents with contracting features such as tallness and shortness are involved in monohybrid cross, the offspring in the first filial generation are usually
A. pure breed.
B. heterozygous dominance.
C. homozygous recessive.
D. mutant.
38. The precondition for transfusion of blood to an accident victim is
A. seeking the consent to his parents.
B. ascertaining the religious belief of the victim.
C. cross-matching the blood group of the donor with that of the accident victim.
D. curing the donor of any disease traced in his blood.
39. Cross-breeding is a way of
A. developing superior varieties of plants only.
B. developing superior varieties of animals only.
C. developing disease-resistant varieties only.
D. applying the principles of heredity in agriculture.
40. The table below indicates the result of an experiment during which grains of different colours in two maize cobs were counted.
| Maize cobs | Colours of maize grains | ||
| White | Pink | Red | |
| i. | 30 | 60 | 30 |
| ii. | 50 | 99 | 49 |
Which of the following ratios agrees with the result?
A. 9:3:3.
B. 1:2:1.
C. 1:3:1.
D. 2:1:1.
43. Which of the following diseases or disorders can be prevented by the application of the knowledge of
heredity through marriage counselling?
A. Sickle cell anaemia.
B. Haemophilia.
C. Diabetes mellitus.
D. Colour blindness.
44. Agglutination occurs in blood transfusion when the
A. donor and the recipient belong to the same blood group.
B. Same antibodies from donor and recipient fuse together.
C. donor and the recipient belong to different races.
D. recipient is not a universal recipient.
45. A man with heterozygous genotype for blood group B marries a woman with heterozygous A, what
percentage (%) of their children would be universal donor? A man with heterozygous genotype for blood
group B marries a woman with heterozygous A, what percentage (%) of their children would be universal
donor?
A. 50%.
B. 25%.
C. 15%.
D. 10%.
Study the genetic cross below showing the inheritance of blood groups
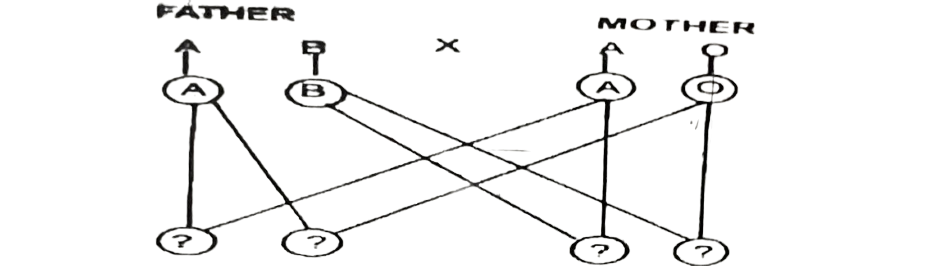
46. From the cross above which of the following F offspring does not belong to the father?
A. AA.
B. AO.
C. OB.
D. OO.
47. In an individual who is heterozygous for a particular character, the hereditary factor that is always
expressed is described as
A. allele.
B. sickle-cell gene.
C. dominant gene.
D. chromosome.
48. A person with blood group B can only donate blood to individuals with blood groups
A. A and B.
B. B and AB.
C. O only.
D. B only.
49. During blood transfusion, agglutination could be prevented if a patient having blood group O is given
blood from group
A. AB.
B, A.
C. O.
D. B.
50. If two parents are sickle cell carriers then their genotypes would be
A. Hb^ Hb^ and Hb Bb.
B. Hbs Hbs and Hbs Hbs.
C. Hb^ Hbs and Hb Hbs.
D. Hb Hb and Hb^ Hb^.
51. During blood transfusion, agglutination may occur as a result of the reaction between
A. similar antigens and antibodies.
B. contrasting antigens and antibodies.
C. two different antigens.
D. two different antibodies.
52. In man haemophilia is recessive and sex linked. The probability of a carrier mother and a normal father having a haemophilic male is
A. 14.
B. 1/8.
C. 23.
D. 12.
53. In which of the following is the knowledge of genetics not applicable?
A. Development of high-yielding varieties.
B. Preservation of seeds.
C. Development of early maturing varieties.
D. become eliminated.
54. Which of the following blood group(s) is/are the universal donor(s)?
A. O.
B. A.
C. B.
D. AB.
55. Assuming that ‘A’ is gene for normal skin and it is dominant, while ‘a’ is gene for albinism and it is
recessive, what is the likely genotype of a couple which had 50% normal and 50% albinos?
A. AA.Aa.
B. AA.aa.
C. Aa, Aa.
D. Aa, aa.
56. If a black guinea pig of genotype BB, is crossed with a white guinea pig of genotype bb, what will be the phenotype of the F1 generation
A. Half of the offsprings would be black while the other half would by white.
B. All the offsprings would be black. C. All the offsprings would be grey.
D. One-third of the offsprings would be black while two-third would be white.
57. If a cross is made between a pure-breeding red flowered plant and a pure-breeding white flowered
plant where R is dominant for red flower and r is recessive for white, the most likely result of F,
generation will be
A. 75% red flowers and 25% white flowers.
B. all red flowers.
C. 75% white flowers and 25% red flowers.
D. 50% red flowers and 50% white flower.
58. A man with blood group A (TAP) married a woman he with blood group O (pp). Which of the following is the probable ratio of the blood groups of the offspring?
A. 1:1.
B. 3:1.
C. 2:1.
D. 1:2:1.
59. Which of the following statements is true about blood groupings?
A. Group AB can donate blood to all other groups.
B. Group O are universal recipients. C. Group A has A antigen in its plasma.
D. Group O has no antigen.
The table below is a Panetta square for sexarab determination in man. Use it to answer questions 60 &
61.

60. Which of the following determines a normal male offspring?
A. X.
B. Y.
C. XX.
D. XY.
61. What is the theoretical probability that a normal male child will be born?
A. 1/2.-
B. 14.
C. 13.
D.1.
62. What will be the genotypic ratio when two wheterozygous red pea plants are crossed?
A. 1:0.
B. 1:2:1.
C. 2:1.
D. 3:1.
63. Heterozygous tall plants were crossed with pure-breeding dwarf plants of the same species. What were the approximate percentages of the offspring?
A. 100% tall 0% dwarf.
B. 75% tall 25% dwarf.
C. 50% tall 50% dwarf.
D. 25% tall 75% dwarf.
64. In human beings the albino trait is recessive and the normal skin colour is dominant. Therefore the
probability of parents that are heterozygous for albinism, having an albino child is
A.1/4.
B. 1/2.
C. 1/3.
D. 2/3.
65. Which of these statements is correct in the human ABO blood grouping system?
A. B is recessive.
B. A is dominant over B.
C. O is recessive.
D. O has antigens A and B.
66. The blood group in humans referred to as a universal recipient is
A. O.
B. A.
C. B.
D. AB.
67. If a heterozygous red flowered plant, (Rr) was self- fertilized, the offspring would be expected to be A. all red flowered plants.
B. all white flowered plants.
C. red flowered, white flowered plants.
D. white flowered red flowered plants.
68. In a plant of genotype Tt, what is the probability that a gamete will contain gene t?
A. 1/2.
B. 3/4.
C. 1/8.
D. 16.
69. If a pure breeding white cat (homozygous dominant) mates with a pure breeding black cat (recessive), what would be the fur colour of the F generation
A. Homozygous white.
B. Homozygous black.
C. Heterozygous white.
D. Heterozygous black.
70. In a cross involving a heterozygous red flowered plant (Rr) and a white flowered plant (rr). what is the
probability that the offspring will be Rr?
A. 1.
B. /.
C. 4.
D. 2.
71. Which of the following pairs of scientists discovered the Rhesus factor in human blood?
A. Hooke and Lavine.
B. Darwin and Landsteiner.
C. Landsteiner and Lavine.
D. Hooke and Darwin.
Use the following information to answer Questions 72 and 73. In an experiment, a red-flowered plant was
crossed with another red-flowered plant and the following results were obtained: 448 red flowers and 154
white flowers in the F1, generation M22
72. Which of the following represents the genotypes of the parents if R is for red gene and r for white gene?
A. RR 2x Rr.
B. RR x rr.
C. rr x rr.
D. Rr x Rr.
73. Which of the following represents the phenotypic ratio of the above genetic cross?
A. 1:2:1.
B. 4:1.
C. 3:1.
D. 2:2.
74.
| Donor | Recipient | |
| I | toto | TATA |
| II | tBto | TBTB |
| III | TATA | TATB |
| IV | TATA | toto |
| V | toto | TBTB |
In which of the underlisted blood grouping is agglutination likely to occur during transaction
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
75. Which of the following represents the phenotypic ratio, when a plant Rr is crossed with another plant Rr, assuming that the gene R for round seed is dominant and wrinkled r is recessive?
A. 3:2.
B. 1:2:1.
C. 2:2:1.
D. 3:1.
76. An individual with blood group AB can receive blood from those in blood group(s)
A. AB only.
B. A and B only.
C. B only.
D. AB and O only.
77. The genotypic ratio of 1:2:1 in the offspring of a hybrid cross illustrates the law of
A. use and disuse.
B. dominance.
C. segregation.
D. linkage.
78. Which of the following traits may not be important in marriage counselling?
A. Sex-determination.
B. Sickle-cell anaemia.
C. Rhesus factor.
D. Colour of skin.
79. One of Mendel’s experiments was repeated by crossing a red variety of pepper with that of a yellow variety which produced all red offspring. The red offspring were then self pollinated and these produced both red and yellow pepper. The yellow colour can be said to be
A. dominant to red.
B. recessive to red.
C. homozygous to red.
D. heterozygous to red.
80. One of the factors that must be considered for safe blood transfusion is
A. social class of the donor.
B. age of the recipient.
C. rhesus factors of the donor and the recipient.
D. nationality of the donor.
81. When Mendel crossed round seeds with wrinkled seeds of Pea Plant, what was the ratio of wrinkled
seeds to round seeds in the F2, plants?
A. 3: 1.
B. 2: 1.
C. 1: 3.
D. 1:2.
82. If the pink colour of a petal is dominant over white what would be the colour of the flower of the F
generation when a pure pink flowered plant is crossed with a white flowered plant
A. Purple.
B. Pink.
C. White.
D. Yellow.
83. One of the applications of variation is in
A. determining the size and weight of individuals.
B. determining paternity.
C. conservation of wild life.
D. controlling of disease vectors.
84. In the F1, generation of Mendel’s experiment obtained by crossing pea plants of long stems with those of short stems, what was his observation?
A. some were short while others were long.
B. all were long. C. half of them were long while half were short.
D. three-quarters were long while one-quarter were short.
85. In Mendel’s experiments, it was discovered that the F generation of a cross between a brown cock and a
A white hen were all brown because the gene for the A. brown colour was recessive.
B. white colour was dominant.
C. brown colour was dominant.
D. white colour did not combine.
86. In a complete dominance monohybrid cross between a pure breeding yellow flowered plant Y and a pure breeding white flowered plant y, the result of the first filial generation is
A. 50 % yellow flowers.
B. 75 % yellow flowers.
C. all yellow flowers.
D. all white flowers.
87. A man whose blood group is heterozygous B is married to a woman whose blood group is also heterozygous B. Which of the following statements is correct about the blood group of their four offspring?
A. Three of them belong to blood group B.
B. Three of them belong to blood group O.
C. None of them belongs to blood group O.
D. Two of them belong to blood group B.
88. The cross between RrTt and rrtt where R is a gene for red colour and T for tallness will result in
A. all the offspring being tall with red fruits.
B. 25 % tall with red fruits.
C. 50 % tall with red fruits.
D. 75 % tall with red fruits.
89. A child that can receive blood donation from anybody belongs to the blood group
A. O.
B. A.
C. B.
D. AB.
The diagram below is an illustration of a cross between plants A and B of the same species. Study it and answer questions 90 and 91.
90. If the F generation are plants with high yield and resistance, the genotype of the F, generation plants
would be
A. YYRR.
B. YyRr.
C. yyRr.
D. yyrr.
91. The process that gave rise to the F, generation is
A. Self fertilization.
B. Cross fertilization.
C. Out-breeding.
D. Test cross.
92. A mixture of blood with antigen A and blood 28 containing antiborly a will
A. lead to agglutination.
B. facilitate dissolution of clot.
C. have no effect on blood composition.
D. change the blood group.
93. Plants suitable for experiments in genetics must not
A. produce numerous seeds within a short time.
B. have a small number of chromosomes.
C. have a relatively short life cycle.
D. produce one generation in a long period.
94. Which of the following statements about sickle cell anaemia is correct?
A. It is caused by sex-linked genes
B. It is more common in males than in females
C. Two sickle cell carrier parents may have a sickling child
D. It is caused by recessive genes
95. In humans, pointed eyebrows (B) is a dominant trait over smooth eyebrows (b). A student and the mother have smooth eyebrows while the father has pointed eyebrows. What is the genotype of the father? A. BB
B. Bb
C. bb
D. BBbb
96. A woman with Rhesus negative blood group was advised not to marry a man with Rhesus positive blood group because
A. it will hinder her from having blood transfusion from her husband.
B. it will result in sickness and probably death of the offspring.
C. her children may all resemble her husband.
D. it may affect her childbearing ability.
97. Two tall plants were crossed and all the F, plants were tall. When the F, plants were selfed, some of the F2 plants were tall while others were short. What are the possible genotypes of the original plants?
A. Tt and tt
B. TT and TT
C. tt and tt
D. TT and Tt
98. Which of the following statements best describes a test cross? It is
A. to determine the genotype of an individual whose phenotype is known
B. to determine the phenotype of an individual whose genotype is known
C. between the progeny of parents to ascertain their external expressions
D. between two homozygous recessive individuals to confirm the genotypes of the offspring
99. Which of the following statements about sex-linked traits is not correct?
A. Males inherit sex-linked traits from their fathers
B. Sex-linked traits are more common in males
C. Females can be carriers because they can be heterozygous for the trait
D. Males are never carriers since they only receive one sex chromosome
100. When two carriers of sickle cell anaemia produce an offspring, the probability of the offspring being a sickler is
A. 3/4.
B. 1/4.
C. 1/2.
D. 2/3.
101. A Rhesus negative woman may experience stillbirth of the second child that is Rhesus positive because
A. the woman is susceptible to diseases during pregnancy.
B. the blood of the foetus might clump.
C. they have poor circulatory system.
D. the foetus is deprived of nourishment.
102. Paternity disputes could be resolved accurately through
A. finger printing.
B. blood group.
C. DNA test
D. tongue rolling.
The illustration below is a genetic diagram. Study it and answer questions 103 to 105.
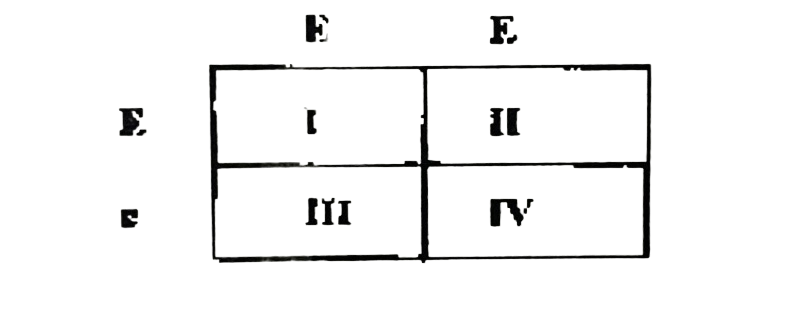
103. What is the name of the genetic diagram?
A. Genetic cross.
B. Punnett square.
C. Inheritance diagram.
D. Genetic square.
104. What do the labels I, II, III and IV respectively represent?
A. EE, EE, EE and EE.
B. Ee, Ee, EE and Ee.
C. EE, EE, Ee and Ee.
D. EE, EE, Ee and ee.
105. The genotypic ratio of the offspring in the genetic diagram is
A. 1:1.
B. 1:2:1.
C. 1:3.
D. 4:0.
106. What is the probability that a pregnancy would result in a male child?
A. 1.
B. 3/4
C. 1/2
D. 1/4
THEORY
1. A survey to determine blood groups was carried out on 250 people living in a community. The results are represented in the table below
| Blood group | Percentage |
| A | 8.0 |
| B | 14.0 |
| AB | 32.8 |
| O | 45.2 |
(a) Explain the term co-dominance.
(b) Calculate the number of individuals with co-dominant blood group.
(c) What is the total number of individuals in the table that are able to donate blood to an accident victim with blood group B?
(d) A man whose blood group is heterozygous A is married to a woman whose blood group is AB. With the aid of a genetic diagram, suggest the possible blood groups of their children.
2. (a) Explain the term agglutination as used in blood transfusion
(b) The table below represents blood transfusion between blood donors and recipients. Copy and complete the table using the keys (+) to represent compatibility and (-) to represent incompatibility
| Recipient | |||||
| Donor | A | AB | B | O | |
| A | |||||
| AB | |||||
| B | |||||
| O | |||||
3. A child belongs to blood group O and the mother belongs to group B. With the aid of a genetic cross, state the possible blood groups of the father.
4. Explain briefly how fingerprinting can be used to detect crime.
5. (a) State four advantages a farmer may hope to derive in cross-breeding two different breeds of cows. (b) State three applications of the knowledge of genetics in medicine.
6. In garden pea seeds, smooth seed coat is dominant over rough seed coat. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the result expected if a homozygous rough pea is crossed with a smooth seed coat plant whose parents were rough coated.
7. In a mango plant, the allele for bean-shaped seed is r and is recessive to round-shaped seed R. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the genotypes of the offspring if:
(i) a homozygous bean-shaped parent is crossed with a homozygous round shaped parent.
(ii) a heterozygous bean-shaped parent is crossed with a heterozygous round shaped parent.
8. A woman with blood group ‘A’ (heterozygous) claimed that her son who has blood group ‘O’ was fathered by Mr. James who has blood group ‘A’ (homozygous). With the aid of suitable genetic diagrams (i) prove or disprove the woman’s claim;
(ii) Give reasons to support your answer.
9. In a breeding experiment, a homozygous black dog (BB) was crossed with a homozygous white dog (bb) to produce black puppies in the first filial generation (Fr). The second filial generation produced a total of two hundred and forty (240) black and white puppies. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine:
(i) the number of white puppies
(ii) the number of black puppies in the second filial generation.
10. (a) Two heterozygous yellow flowers are crossed. Using a genetic diagram, state the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the first filial generation.
(b) State four transmittable characters in plants to
11. (a) In a monohybrid cross between a pure breeding plant that produces blue flowers and a pure breeding plant that produces white flower, the F1 generation produced only blue flowers. By means of labelled cross diagrams, state the type of flowers you would expect if the F1 generation is
(i) self-pollinated
(ii) cross-pollinated with a pure breeding plant that produces white flowers. Give reasons for your answers in (a) (i) and (ii).
12. (a) State three ways in which genetics has contributed to improvement of agriculture.
(b) A homozygous tall parent was crossed with a homozygous short parent with another homozygous short individual Illustrate the crosses with suitable diagrams The offspring in Fi generation were all tall. An offspring of F1, generation was then crossed with another homozygous short individual:
(i) illustrate the crosses with suitable diagrams
(ii) What is the phenotypic ratio of offspring in the F2 generation?
(iii) What is the genotypic ratio of offspring in the F2 generation?
(iv) What is the probability that an individual that has genotype Tt will produce a gamete with Ti gene? Briefly explain your answer.
13. Explain why blood groups A and B in man can exist both in heterozygous and homozygous conditions while blood group O can only exist in homozygous state.
14. (a) Two varieties of maize, one with yellow (Y) grains and the other with purple (y) grains were crossed and all their offspring’s had yellow grains. When the offspring’s were crossed with the parent variety with purple grains, half of the resulting offspring’s had yellow grains, while the other half had purple grains. Using labelled diagrams only; Deduce the genotype of the grains of the first filial generation,
(b) Show the results of the cross between the first filial generation and the parent purple variety.
(c) Mention two ways in which the application of genetics is beneficial to agriculture.
15. How do you determine whether a man with blood group ‘O’ and married to a woman with blood group ‘AB’ is the father of a child with blood group ‘AB’ born to them?
16. A pure breeding brown coloured rat, BB was crossed with a pure breeding white rat bb. By means of diagram only, show the genotypes of the offspring up to the second filial generation.
17. Use the information below to answer the questions (a) (i) & (ii): hat Hb^ represents normal haemoglobin, Hb represents sickied haemoglobin.
(a) A female heterozygote for sickle cell married a sickler. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the:
(i) possible genotypes of their offspring
(ii) phenotypic ratio of the offspring.
(b) Explain briefly the reason why a Rhesus negative woman married to a Rhesus positive man might lose her second pregnancy.
18. Explain briefly: the reason blood group O in humans can only exist in homozygous form while blood groups A and B can exist both in homozygous and heterozygous forms,
19. (a) Complete the following Punnett squares of a dihybrid cross between two rats. One has black fur (BB) and short tail (tt), the other has brown fur (bb) and long tail (TT).
| X | Bt | |||
| bT | ||||
(b) How many of the offspring will have:
(i) black fur and short tail;
(ii) brown fur and long tail;
(iii) black fur and long tail;
(iv) brown fur and short tail?


