Introduction:
The respiratory system is essential for the survival of organisms, facilitating the exchange of gases—primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide—between the body and the environment. Understanding the structures and mechanisms involved in respiration across different organisms is crucial for students preparing for the WAEC Biology examination.
Key Concepts:
1. Definition of Respiration:
Respiration is the biochemical process by which organisms convert glucose and oxygen into energy (ATP), releasing carbon dioxide and water as by-products.
2. Types of Respiration:
- Aerobic Respiration: Occurs in the presence of oxygen, producing a large amount of energy.
- Anaerobic Respiration: Occurs in the absence of oxygen, yielding less energy and producing lactic acid or ethanol as by-products.
3. Human Respiratory System:
- Nasal Cavity: Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air.
- Pharynx and Larynx: Pathways for air to reach the lungs; the larynx also houses the vocal cords.
- Trachea: A tube that conducts air to the bronchi; lined with cilia and mucus to trap particles.
- Bronchi and Bronchioles: Branching tubes that distribute air within the lungs.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs; surrounded by capillaries.
- Diaphragm and Intercostal Muscles: Muscles that facilitate breathing by changing the volume of the thoracic cavity.
4. Mechanism of Breathing:
- Inhalation: Diaphragm contracts and flattens; intercostal muscles raise the rib cage, increasing thoracic volume and drawing air into the lungs.
- Exhalation: Diaphragm relaxes and domes upward; intercostal muscles lower the rib cage, decreasing thoracic volume and expelling air from the lungs.
5. Respiratory Structures in Other Organisms:
- Fish: Use gills to extract oxygen from water.
- Amphibians (e.g., frogs): Respire through skin, lungs, and buccal cavity.
- Insects: Utilize a tracheal system with spiracles for gas exchange.
- Plants: Exchange gases through stomata in leaves and lenticels in stems.
6. Characteristics of Respiratory Surfaces:
- Large surface area to maximize gas exchange.
- Thin walls to facilitate diffusion.
- Moist surfaces to dissolve gases.
- Rich blood supply (in animals) to transport gases.
- Ventilation mechanisms to maintain concentration gradients.
7. Disorders of the Respiratory System:
- Asthma: Inflammation and narrowing of airways, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, often due to infection or irritation.
- Pneumonia: Infection causing inflammation of the alveoli, leading to impaired gas exchange.
- Emphysema: Damage to alveolar walls, reducing surface area for gas exchange.
8. Differences Between Gaseous Exchange and Respiration:
| Feature | Gaseous Exchange | Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical process of gas movement across respiratory surfaces | Biochemical process of energy production in cells |
| Location | Respiratory organs (e.g., lungs, gills) | Cellular organelles (e.g., mitochondria) |
| Energy Production | Does not produce energy | Produces ATP (energy) |
| Oxygen Utilization | Involves oxygen intake | Uses oxygen to oxidize glucose |
| By-products | Carbon dioxide expelled | Carbon dioxide and water produced |
Study Tips:
- Understand Terminology: Familiarize yourself with key terms such as alveoli, diaphragm, and trachea.9as
- Use Diagrams: Practice drawing and labeling the human respiratory system and other organisms’ respiratory structures.
- Compare Systems: Create comparison tables to highlight differences and similarities between respiratory systems of various organisms.
- Review Past Questions: Use the questions below for study and practice.
- Engage in Group Discussions: Discussing topics with peers can enhance understanding and retention.
Conclusion:
A thorough understanding of the respiratory system is essential for success in the WAEC Biology examination. By mastering the structures, mechanisms, and variations of respiration across different organisms, students can appreciate the complexity and efficiency of this vital biological system.
Objectives:
1. The diagrams below are parts of a human lung. Which of the labelled parts is diagram Z taken from?
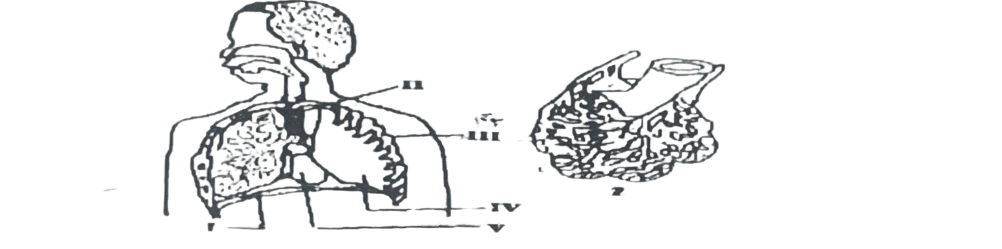
A. II. B. III. C. IV. D. V.
2. In the adult frog gaseous exchange takes place through the
A. buccal cavity, skin and lungs. B. buccal cavity, skin and spiracles. C. gills, skin and buccal cavity. D. tympanic membrane, lungs and gills.
3. Which of the following structures is used for respiration in insects?
A. Lungs. B. Thorax. C. Cuticle. D. Spiracles.
4. The cells and tissues of the nose, throat, chest diaphragm and lungs form the
A. circulatory system B. respiratory system transport system. D. digestive system.
5. Inhaled air is made warm and moist in the
A. epiglottis. B. nasal cavity. C. trachea. D. mouth.
6. Which of the following structures is not involved in respiration?
A. Lung books. B. Mouth. C. Stomach. D. Trachea.
7. Which of the following structures would carry out respiration?
A. germinating cowpea. B. decolorized leaf. C. dry leaf. D. boiled cowpea.
8. Which of the following organs are used for gaseous exchange in a mature toad?
A. Gills, lungs and eardrum. B. Lungs, mouth and eardrum. C. Mouth, skin and gills. D. Skin, lungs and mouth.
9. The structures for gaseous exchange in breathing roots are
A. stomata. B. lenticels. C. cuticle. D. mitochondria.
10. The exchange of gases between the environment and the respiratory organs of vertebrates is referred to as
A. inhalation B. respiration. C. expiration. D. breathing.
11. Which of the following actions does not occur during exhalation in man A. Thoracic cavity decreases in regular movements of the diaphragm and the
A. Intercostal muscles. B. vertebral column. C. clavicle. D. pleural cavity.
12. Which of the following statements about the diaphragm of a mammal is not correct? It
A. separates the thorax and the abdomen. B. is a thick layer of muscle. C. is made of epithelial cells. D. is part of the human respiratory apparatus.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 13 to 16
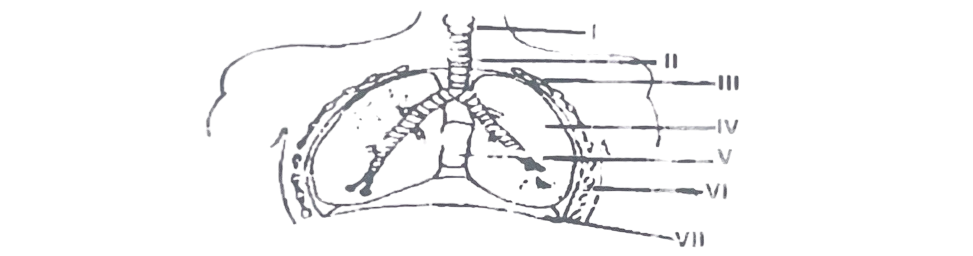
13. The part labelled VII is the
A. pleural cavity. B. lung. C. rib. D. diaphragm.
14. The part labelled I is the
A. epiglottis. B. larynx. C. oesophagus. D. trachea.
15. Exchange of gases takes place in the air sacs contained in the part labeled
A. 1. B. II. C. IV. D. V.
16. During the process of breathing, volume and pressure changes occur as a result of the movement of the parts labeled
A. I and II. B. II and IV. C. III and VII. D. NV and V.
17. The conditions that ensure successful exchange of gases in multicellular organisms include the following except
A. concentration gradient across the respiratory surface. B. presence of thin membrane as the respiratory surface. C. last transportation of absorbed gases. D. presence of small, dry surface area of the respiratory organ.
18. The respiratory organ found in the cockroach is the
A. air sac. B. trachea. C. lung book. D. lung.
19. Which of the following-statements is not correct of respiration?
A. Gaseous exchange occurs by diffusion. B. Oxygen combines with haemoglobin at the respiratory surface. C. Carbon dioxide produced in the tissues is removed by the process of osmosis. D. There are no special organs for respiration.in plants.
20. Gaseous exchange takes place in the adult toad. through the
A. buccal cavity, bladder and lungs. B. buccal cavity, skin and lungs. C. tympanic membrane, lungs and gills. D. buccal cavity, skin and spiracle.
21. Breathing movement in mammals is accompanied by regular movements of the diaphragm and the
A. Intercostal muscles B. Vertebral column C. Clavicle D. Pleural cavity.
22. Which of the following does not occur during inhaling in mammals?
A. Rib cage is raised up. B. Diaphragm contracts and becomes dome shaped. C. Inter-coastal muscle contracts. D. Volume of the thoracic cavity increases
23. The organ located in mammals abdominal cavity just below the diaphragm and lying on top of the stomach is the
A. Bladder. B. Intestine. C. Liver. D. Pancreas.
24. In plants, respiration occurs in
A. Mesophyll cells only. B. The root only. C. The stomata and lenticels only. D. Living cells.
25. Which of the following structures is associated with respiration in insects?
A. Air sac. B. Spiracle. C. Lung D. Alveolus.
26. Which of the following organisms and organs of gaseous exchange are not appropriately matched?
A. Earthworm body surface. B. Fish-gills. C. Adult toad gills. D. Grasshopper-trachea,
27. Which of the following organs is specially adapted for gaseous exchange in aquatic organisms?
A. Lung. B. Trachea. C. Gills. D. Tracheoles.
28. The products of respiration are
A. nitrogen and water B. nitrogen and carbon dioxide. C. water and oxygen. D. carbon dioxide and water.
29. Gaseous exchange occurs through the following structures in some organisms except
A. spiracle and tracheae. B. alveoli and lungs. C. stomata and lenticels. D. chloroplast and plastids.
30. Which of the following organisms respires through the body surface
A. Man. B. Fish. C. Tridax. D. Amoeba.
31. Which of the following does not happen during inspiration?
A. Intercostal muscles contract. B. Ribs move forward. C. Thoracic cavity increases. D. Diaphragm relaxes.
32. Which part of the gill of-fish is involved in gaseous exchange?
A. Gill slits. B. Gill bars. C. Gill covers. D. Gill filaments.
33. Which of the following pairs of structures does not perform similar functions?
A. Lungs and spiracles. B. Root hair and mammalian hair. C. Feathers and scales. D. Contractile vacuole and kidney.
34. The effect of the contraction of the muscles of the arts diaphragm is that
A. the volume of the thoracic cavity increases. B. more carbon dioxide is expelled through the nostrils. C. the rib cage is drawn inwards. D. the intercostal muscle becomes relaxed.
35. Which of the following has the most primitive respiratory system?
A. Rat. B. Fish. C. Toad. D. Grasshopper.
36. The mechanism of gaseous exchange in living organisms is essentially by
A. osmosis. B. inhalation. C. diffusion. D. exhalation.
37. The upper part of the trachea in mammals is called
A. palate. B. epiglottis. C. larynx. D. glottis.
38. Which of the following structures of the human body 1. provides the best surface for diffusion?
A. Skin. B. Stomach. C. Aveolus. D. Oesophagus.
39. Pneumatophores are essential for
A. nutrition. B. movement. C. breathing. D. growth.
The graphs below show the results of experiments which investigated the effect of temperature and oxygen on the rate of uptake of certain ions labelled X and Y by a plant root. Use them to answer question 40
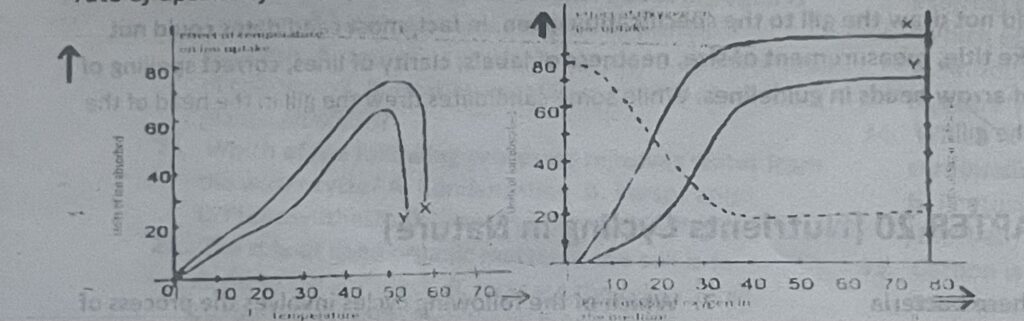
40. Which of the following conclusions cannot be drawn from the graphs?
A. Ion is taken up more rapidly at suitable temperature. B. Suitable oxygen concentration increases ion uptake. C. Ion uptake requires energy from aerobic respiration of sugar. D. The S quantity of ions absorbed is inversely proportional to the quantity of carbohydrates (sugar) synthesized.
41. Terrestrial plants exchange gases through the following except
A. chloroplast. B. stomata. C. lenticels. D. root-cells.
42. The products of tissue respiration are
A. glucose, oxygen and water. B. oxygen, water and energy. C. glucose, carbon dioxide and energy D. water, carbon dioxide and energy.
43. The respiratory organ of a cockroach is the
A. Air Sac B. Trachea. C. Lung book. D. Lung.
44. Oxygen comes out of the stomata during photosynthesis through the process known as
A. Diffusion. B. Transpiration pull C. Osmosis D. Active transport.
Use the following processes to answer questions 11 and 12.
I – Ribs move upward and outward
II – Diaphragm relaxes
III – Volume of thorax increases
IV – Air is forced out of the lunges
45. Which of the processes take place during inspiration?
A. I and ill only B. II and III only C. II and IV only. D. III
46. Which of the processes is a direct result of contraction of the intercostal muscles?
A. I B. II C. III D. IV
The diagram below is an illustration of some structures housed for gaseous exchange in humans. Study it and answer questions 47 and 48.
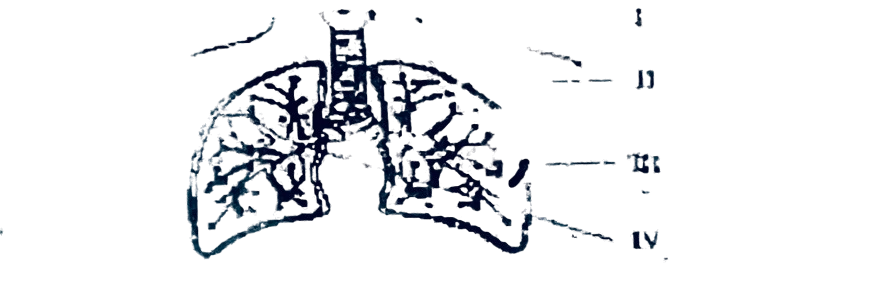
47. The parts labelled 1, II, III and IV respectively are
A larynx, bronbronchiole and trachea. B bronchus bronchiole trachea and larynx. C. bronchiole, trachea, bronchus and larynx. D larynx, trachea, bronchiole and bronchus.
48. The part labelled III would be found in the
A. heart. B. lung. C. kidney. D. sternum.
THEORY
1. (a) Explain the term residual air (b) What is the importance of residual air to mammals? (c) State four characteristic features associated with respiratory structure.
2. Describe the mechanism of opening and closing of the stomata.
3. (a) Describe the process of inhalation in man (b) Describe briefly the process of gaseous exchange in the shoot system of flowering plants.
4. (a) Explain the following terms artificial respiration (b) Explain the procedure for administering the mouth-to-mouth method of artificial respiration.
5. (a) (i) What is respiration? (ii) Name two types of respiration (iii) Write in words the equation representing the type of respiration that occurs in the muscle during strenuous exercise. (b)(i) Make a large labelled diagram 8 cm to 10 cm long of the human respiratory system to show the internal structures, (ii) Name two diseases that can affect the above mentioned system. (c) Mention the structures used for gaseous exchange in the following organisms: (i) Amoeba; (ii) Cockroach; (iii) White mangrove; (iv) Hibiscus.
6. (a) Briefly explain the term respiration (b)(i) Outline the mechanisms involved in: (i) inhalation; (ii) exhalation in human beings.
7. (a) (i) Complete the table below with the respiratory surface of each of the listed organisms.
| Organisms | Respiratory Surface |
| Tadpole (2 days old) | |
| Cockroach | |
| Domestic Fowl | |
| Talinum | |
| Earthworm | |
| Amoeba |
(ii) State five characteristic features of respiratory surfaces in organisms. (b) Make a drawing, 4 cm – 6 cm long of the respiratory organ in Tilapia and label fully.


