Introduction:
Growth is a fundamental characteristic of all living organisms. In biology, growth refers to the irreversible increase in size and dry mass of an organism, resulting from the assimilation of materials into its body. This process involves various mechanisms and is influenced by both internal and external factors.
Key Concepts:
1. Definition of Growth:
Growth in living organisms is the irreversible increase in size and dry mass, resulting from the assimilation of materials into the body. It involves the synthesis of new protoplasm and is accompanied by cell division, enlargement, and differentiation.
2. Processes Involved in Growth:
- Cell Division: The process by which a parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells, leading to an increase in cell number.
- Cell Enlargement: The increase in the size of individual cells, contributing to the overall growth of the organism.
- Cell Differentiation: The process by which unspecialized cells become specialized to perform specific functions, contributing to the development of tissues and organs.
3. Types of Growth:
- Primary Growth: Involves the elongation of the plant body, resulting from the activity of apical meristems.
- Secondary Growth: Involves the thickening of the plant body, resulting from the activity of lateral meristems.
4. Hormonal Control of Growth:
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating growth processes:
- Auxins: Promote cell elongation and are involved in phototropism and gravitropism.
- Gibberellins: Stimulate cell division and elongation, promoting growth in stems and fruits.
- Cytokinins: Promote cell division and delay senescence.
- Abscisic Acid: Inhibits growth and promotes seed dormancy.
5. Factors Affecting Growth:
Several factors influence the rate and pattern of growth:
- Genetic Factors: Inherited traits determine the potential growth patterns.
- Environmental Factors: Light, temperature, water, and nutrients affect growth rates.
- Hormonal Factors: The balance of growth hormones regulates various growth processes.
Study Tips:
- Understand Key Terms: Familiarize yourself with terms like cell division, differentiation, and the types of growth.
- Learn Hormonal Functions: Know the roles of different hormones in regulating growth.
- Practice Past Questions: Regularly solve WAEC-style questions to test your understanding.
- Use Diagrams: Draw and label diagrams of plant growth processes to reinforce learning.
Conclusion:
Understanding the processes and factors involved in growth is essential for mastering WAEC Biology. The questions provided above cover crucial aspects of the topic, and practicing them will enhance your comprehension and exam performance.
Past WAEC questions on growth and related topics are available below for you to study with.
OBJECTIVES
1. Growth includes the following processes except
A. differentiation.
B. enlargement.
C. mitosis.
D. meiosis.
2. Two organelles directly involved in mitotic cell division are
A. nucleus and mitochondrion.
B. ribosome and w nucleus.
C. centriole and golgi apparatus.
D. nucleus and centriole.
3. Which of the following structures is only formed during cell division in animal cells?
A. Cell membrane.
B. Cytoplasm.
C. Centro some.
D. Ribosome.
The diagram below represents the phenomenon of growth in a meristematic cell of a plant. Use it to answer questions 4 & 5

4. The part labelled II in the diagram is
A. centriole.
B. chloroplast.
C. chromatid.
D. tonoplast.
5. The part labelled I is called the
A. nucleolus.
B. centromere.
C. centriole.
D. spindle.
6. The graph below represents the growth pattern of an animal. Which of the following groups of animals shows this pattern of growth?
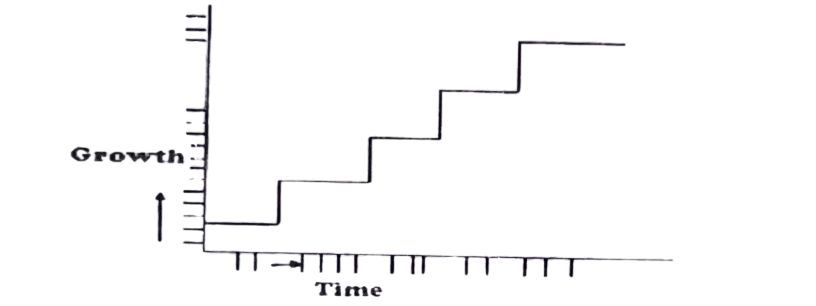
A. Cestoda.
B. Reptilia.
C. Amphibia.
D. Insecta.
7. The following are methods of measuring plant growth except
A. determining the fresh and dry weights of the plant.
B. counting the number of fruits produced.
C. measuring the increase in height of the shoot.
D. measuring the length and breadth of a leaf.
8. The basis of growth involves the following processes except
A. cell reduction.
B. cell division.
C. cell differentiation.
D. cell enlargement.
9. Which of the following processes does not contribute towards growth
A. Cell division.
B. Cell enlargement.
C. Cell differentiation.
D. Cell plasmolysis.
10. The aspects of growth in living organisms include all the following processes except
A. increase in dry weight.
B. reversible increase in size.
C. irreversible Increase in length.
D. increase in number of cells.
11. Which of the following is described as an increase in dry weight?
A. Reproduction.
B. Absorption.
C. Ingestion.
D. Growth.
12. Growth in animals differs from that in plants because growth in
A. plants is intercalary.
B. animals is apical.
C. plants is from within.
D. plants is indefinite.
THEORY
1. (a) What is growth? (b) State two differences each between: growth in plants and animals
2. State two differentes between growth in plants and growth in animals
3. What is the effect of gravity on plant growth?


